Ectopic Pregnancy: Clinical features, causes, prevention and treatment options
Definition of Ectopic Pregnancy
The Ectopic Pregnancy is the implantation of the fertilized egg outside the Uterus where the placenta and fetus are developed.
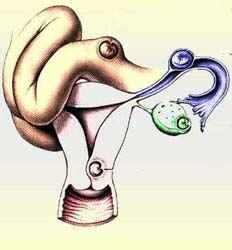 The most common organ of the Ectopic Pregnancy is the fallopian tube, commonly known as tubal pregnancy and represent 95% of cases.
The most common organ of the Ectopic Pregnancy is the fallopian tube, commonly known as tubal pregnancy and represent 95% of cases.
Ectopic pregnancy can also rarely occur in the ovary, in the abdomen "abdominal pregnancy" or in the cervix located in in the lower portion of uterus referred to as cervical pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy occurs in 1-2% of the pregnancies.
Ectopic pregnancy is an important cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
The symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy are similar to those that happen in normal early pregnancy like… headache, nausea, vomiting and breast tenderness.
Other symptoms may as well occur, such as:
- Lower abdominal pain, sometimes may be localized to one iliac fossa. Pain is present in 95% of cases
- Delayed period or irregular menses occur in 75% of cases.
- Light vaginal bleeding usually just spotting. The vaginal bleeding or brownish discharge is due to shedding of the decidua or "decidual cast" when the pregnancy fails.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
- 50% of women with Ectopic Pregnancies have a medical history of Salpingitis or PID. Thus making PID "pelvic inflammatory disease" one of the important causes. Mostly caused by infection of some organisms as gonorrhoea and tuberculosis (TB), Chlamydia, and other infections, such as appendicitis which increase the incidence of ectopic pregnancy.
The ciliated epithelium in the fallopian tube transport the fertilized ovum to the uterus but it can be damaged inflammation increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy. - Previous tubal surgery like tubal sterilization increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy and may reach up to 60%.
Also congenital tubal abnormalities, endometriosis and tubal scarring caused by ruptured appendix or by previous pelvic surgery can cause ectopic pregnancy. - Contraceptive methods: like using progesterone, oral contraceptives and progesterone bearing IUD . The contraceptive method is effective in preventing pregnancy but in case of pregnancy, the risk of Ectopic Pregnancy is high. The components of Progesterone affect peristaltic movement of tubes and slow down the transport of fertilized egg and results in implantation in the tube.
Risk factors for Ectopic Pregnancy
 Maternal age between 35-40
Maternal age between 35-40- Previous ectopic pregnancy increase the risk of recurrence by 10-15%
- Smoking
- Previous salpingitis resulting in tubal damage.
- History of infertility
- Previous pelvic surgery, including sterilization
- Races other than white
- IUD (intra–uterine contraceptive device) users
- Exposure to diethylstilboestrol in utero
Complications of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Rupture ectopic pregnancy with resulting hemorrhage leading to shock. This is the most common complication
- Infertility: occurs in 10-15% of women with history of ectopic pregnancy.
Prevention of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy cannot be prevented but there are important points that should be considered to decrease the incidence of (PID) which as previously mentioned increases the incidence of ectopic pregnancy.
- Avoiding multiple sexual partners
- Using condom during intercourse when one of the partners is infected with (STD)
- Early diagnosis and adequate treatment for (STD)
- Early diagnosis and treatment for (PID)
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Vaginal examination: It may reveal uterine adenexal tenderness.
- Blood test: to check the level of pregnancy hormone (HCG). If the hormone level is not correlated to the normal levels of that stage of pregnancy, it may be ectopic and should be done every 3 days.
- Ultrasound: by using transvaginal ultrasound, the physician can detect embryo in the fallopian tube. But in most cases, the embryo dies early in the process and is too small to be detected by the sonographer. By transvaginal ultrasound, we can detect blood clots as well as tissue that remain from the embryo. Such diagnostic strategies have greatly reduced the use of laparoscopy, but this diagnostic surgical procedure is likely to remain the final diagnostic test if interpretation of the test results is uncertain.
If the pregnancy test or the level of hormone is above 1000 iu/l, with the absence of intrauterine gestational sac it is more likely that we are facing an ectopic pregnancy. - Culdocentesis (historical) this test less commonly performed is used to look for internal bleeding, not useful in detecting an early ectopic pregnancy.
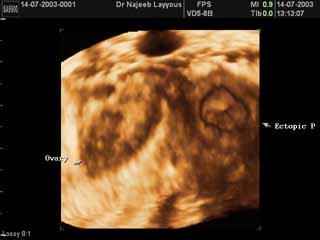 Intact tubal pregnancy
Intact tubal pregnancyTreatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Conservative management of Ectopic Pregnancy
By monitoring ectopic pregnancy, if its size is small and cannot be detected by vaginal u/s and level of HCG very low.
The pregnancy though ectopic can resolve spontaneously with "spontaneous miscarriage through fallopian tube" without any medical or surgical intervention.
Medical treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
The success rate of medical treatment is 80-90%.
In the absence of infertility history, the subsequent conception rate is 80% and the recurrent ectopic pregnancy rate is 11%
This method is safer than surgical treatment. It is used when the embryo is still small and HCG level is not high by using drug (methotrexate) I.M injection and the dose according to BMI and body weight. The drug affects the embryo through blood stream as well as the growth of placental cell. Overtime, The tiny embryo is reabsorbed into your body.
The patient needs blood testing for HCG level to make sure that the pregnancy has been terminated.
The use of metrotrexate may have the following side effects:
- Abdominal pain or cramps
- Nausea And vomiting
- Diarrhea
Note:
During treatment, alcohol should be avoided as well as multivitamins containing folic acid. Some oral intakes can interfere with action of methotrexate.
- You can take paracetamol only as analgesia.
- Preferable to use contraceptives pills for 3-6 months after medical treatment with methotrexate.
Surgical treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Laparoscopic Removal of Ectopic Pregnancy
- The most common surgical treatment used in stable patients in non-emergency cases.
- Less invasive and requires minimal hospitalization. After this operation patient need one week to recuperate.
- Numerous advantages are gained from laproscopic treatment of tubal pregnancy: less time required for surgery, hospital stay at lower costs, with earlier return to activity and improved cosmetic result.
Surgical Laparotomy to Remove Ectopic Pregnancy
- Used when the embryo is too large or when ruptures have already occurred with severe internal bleeding and patient is in shock. After the operation, the patient needs six weeks to recuperate.
- Surgical methods include removal of product of conception, and the tube may be preserved or may need to be removed depending on the situation.
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
